World’s Top 10 Tactical and Combat Drones

High-tech weapons and advanced battle equipment have changed the dynamics of modern warfare. Now militaries can carry out surveillance, and air raids, and attack their enemies from hundreds of miles away using drone technology.
The U.S. Navy was the first one to test the possibility of a pilot-less aircraft in battle scenarios. They began experimenting with radio-controlled (RC) aircraft as early as the 1930s. In 1937, Curtis Aircraft developed N2C-2, the world’s first-ever remotely piloted aircraft. Due to the short range of radio control signals, the N2C-2 could only be controlled through another aircraft, which killed the whole purpose of using drones in military operations.
Some early models of RC aircraft were used by the U.S. Army Air Force for mid-air target practice. Combining the maneuverability of an RC aircraft with the idea of cruise missiles, American aerospace company McDonnell built TD2T Katydid, the first-ever radio-controlled pulsejet-powered target drone that could carry a warhead.
The use of unmanned aerial vehicles in modern security scenarios plays an important role in surveillance, reconnaissance, aerial raids, and finding target coordinates. The ever-evolving drone technology provides a promising replacement for the depleting number of skilled combat pilots all around the world.
IRIA has compiled a list of some of the most technologically advanced combat drones produced by the leading defense manufacturers around the world.
MQ-9 Reaper
Built by the U.S.-based General Dynamics, the MQ-9 Reaper is an advanced long-range, high-altitude surveillance and attack drone. At the time of its induction in 2006, Reaper was the first of its kind hunter-killer unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for long endurance and high-altitude target recognition. It has a large wingspan and long body that allows extended endurance and the ability to carry high volumes of ordnance payload and even cruise missiles.
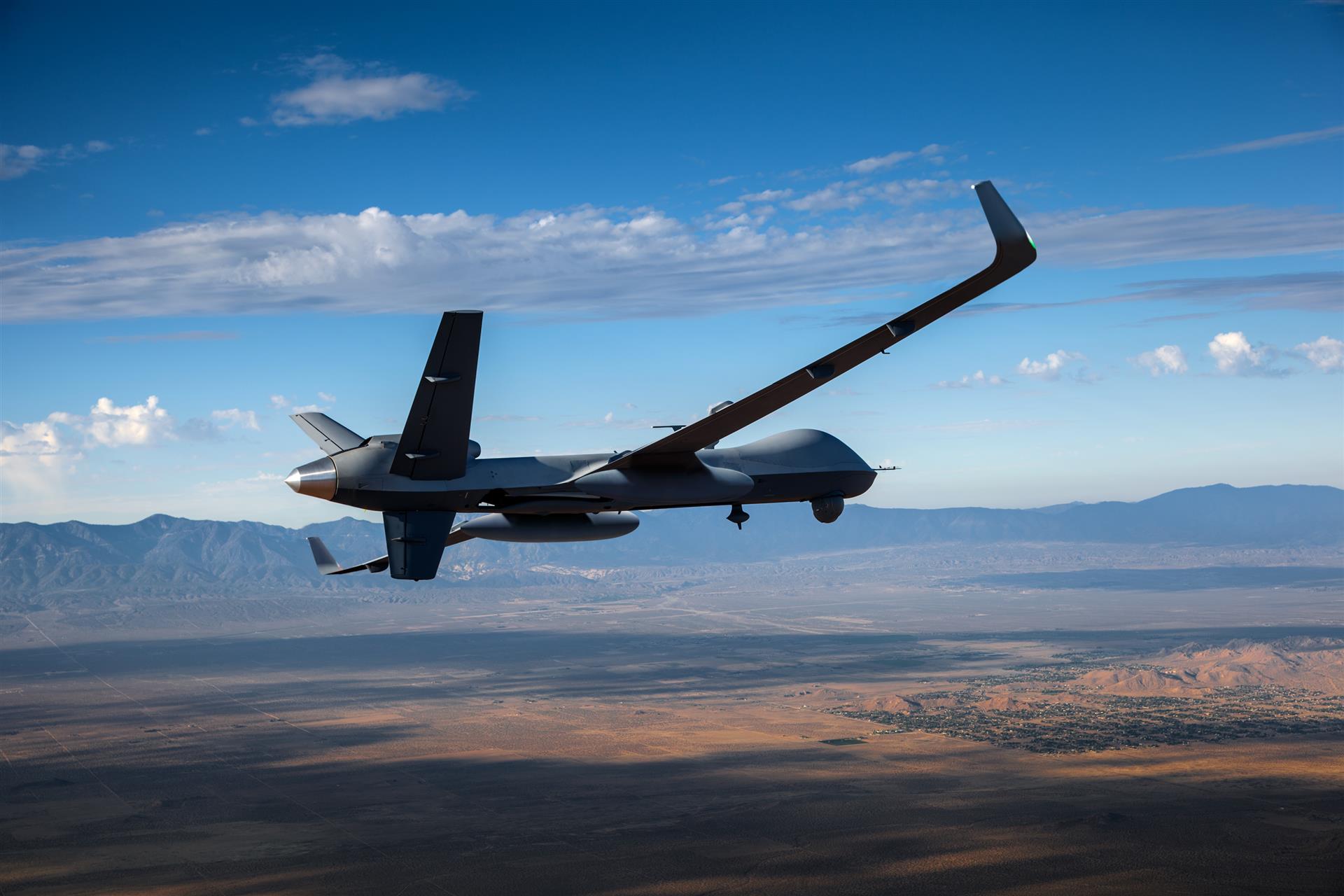 U.S. General Atomics Aeronautical multi-mission MQ-9 Reaper Drone. (Image Credit: General Atomics)
U.S. General Atomics Aeronautical multi-mission MQ-9 Reaper Drone. (Image Credit: General Atomics)
MQ-9 Reaper has a maximum speed of 480 kilometers per hour and a cruising speed of 300 kilometers per hour. Its weaponry is largely made up of air-to-surface missiles AGM-114 Hellfire. An MQ-9 Reaper drone can carry up to eight laser-guided missiles under its wings.
The United States Air Force (USAF) used different variants of the Reaper drones in Afghanistan and Iraq to carry out precise strategic attacks. Different variants of the Reaper drones are also used by militaries in France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, and Australia.
 An MQ-9 Reaper prepares for takeoff at a forward arming and refueling point at the Eglin Air Force Base, Fla. on October 20, 2022. (Image Credit: Air Force Lt. Col. James Wilson/U.S. DoD)
An MQ-9 Reaper prepares for takeoff at a forward arming and refueling point at the Eglin Air Force Base, Fla. on October 20, 2022. (Image Credit: Air Force Lt. Col. James Wilson/U.S. DoD)
Endurance: 27 hours
Payload capacity: 1,701 kilograms (kg)
Maximum speed: 240 KTAS (480 km/h)
Maximum altitude: Up to 50,000 feet (ft)
Primary function: Intelligence collection in support of strike, coordination, and reconnaissance missions.
TAI Aksungur
The Turkish drone industry has emerged as a prominent global leader. One of the most promising products that have come out from Turkey is the Aksungur drone. Developed by the Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI), the Aksungur entered service in 2021. Aksungur drone has been built using the existing technology that TAI employed in its previous successful drone named Anka.
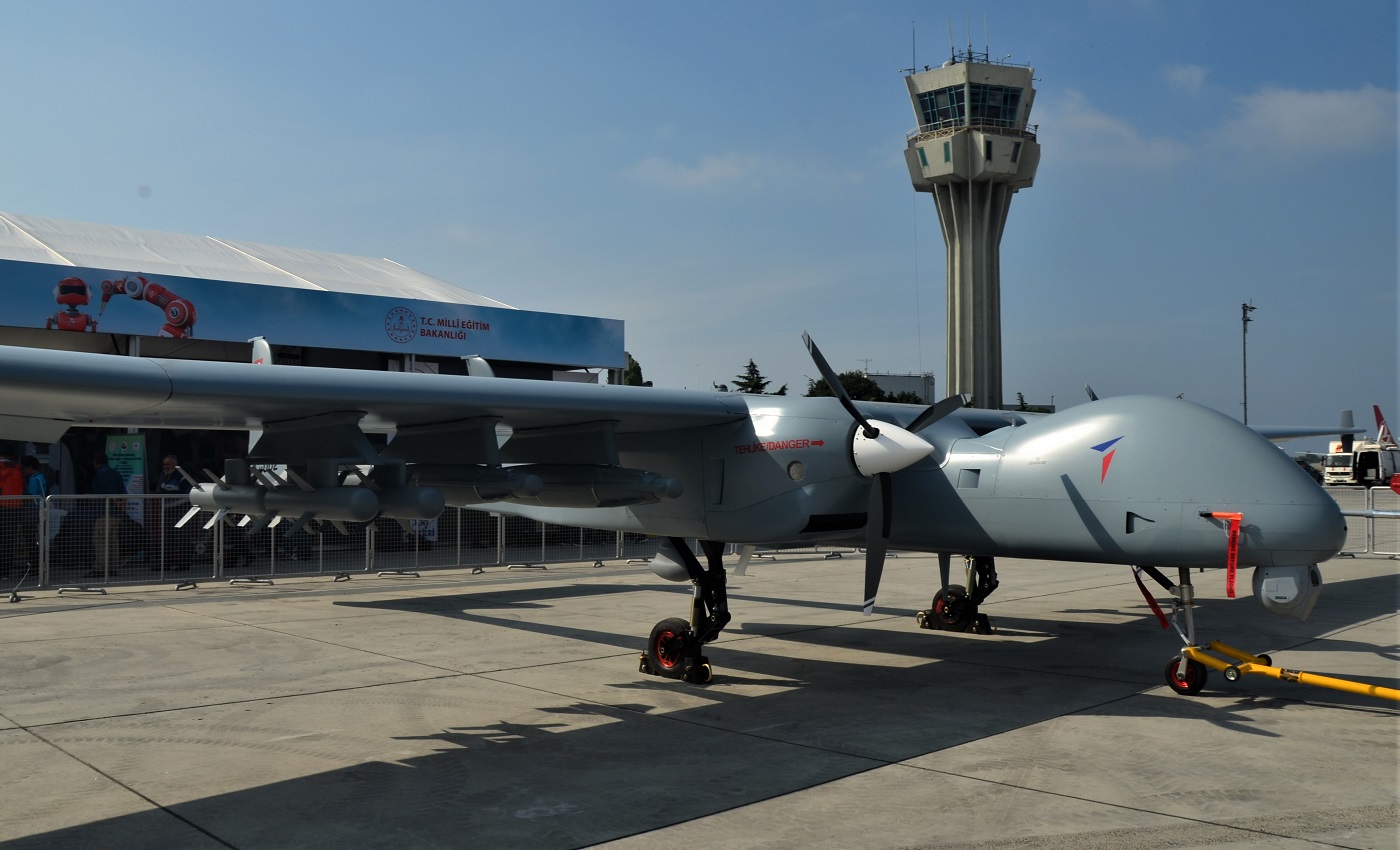 TAI Aksungur combat drone at Teknofest 2019, in Turkiye. (Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
TAI Aksungur combat drone at Teknofest 2019, in Turkiye. (Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Aksungur is a Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE+) class UAV System. The aircraft is 12 meters long with a wingspan that stretches up to 24 meters in width. It is powered by two PD-170 dual-turbocharged diesel engines developed by Turkey’s Tusas Engine Industries (TEI).
The drone is ideal for high-altitude reconnaissance, observation, and destruction of enemy targets. The UAV can carry guided missiles on its six underwing suspension nodes, including guided bombs, and laser-guided munition. So far, Turkish military and naval forces are the only operators of the Aksungur drone, however, due to its low price and manageable maintenance cost, several countries are interested in purchasing the drone.
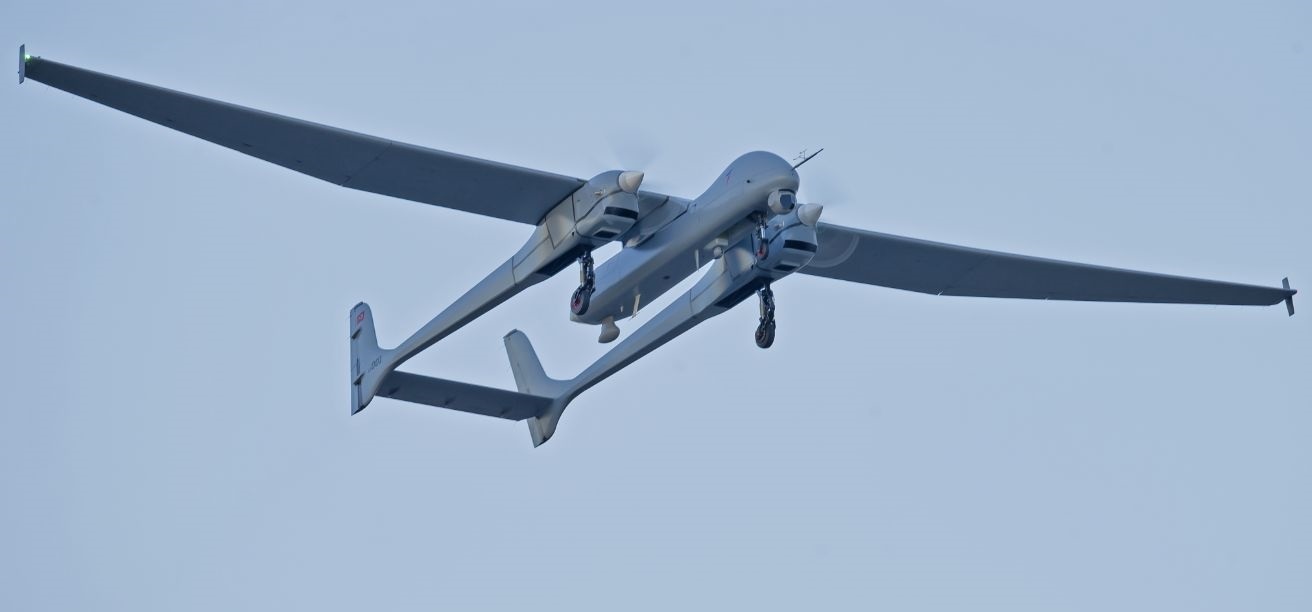 TAI Aksungur medium altitude long endurance UAV system. (Image Credit: Turkish Aerospace Industries)
TAI Aksungur medium altitude long endurance UAV system. (Image Credit: Turkish Aerospace Industries)
Endurance: 50 hours
Payload capacity: 750 kg
Maximum speed: 110 mph (180 km/h)
Maximum altitude: Up to 25,000 ft
Primary function: Day and night Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) and strike missions.
Hongdu GJ-11 Sharp Sword
Different variants of GJ-11 serve as the primary combat drones for the Chinese military. Introduced in 2013, the Hongdu GJ-11 Sharp Sword is a jet-powered stealth drone that carries a wide array of sensors and weaponry. The drone is about 12 meters long and 14 meters wide designed in a single-wing configuration. The tailless design provides extra stealth capabilities and high-speed maneuverability.
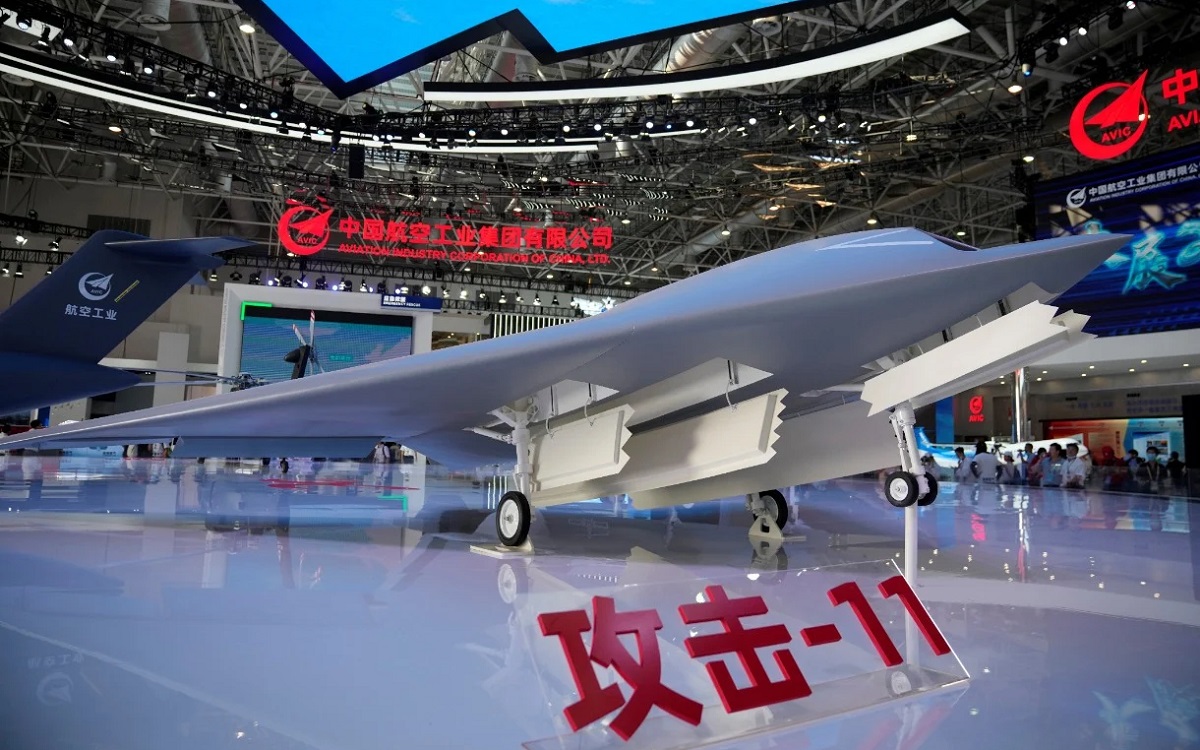 China’s Hongdu GJ-11 combat drone displayed at the Aviation Industry Corporation, pavilion ahead of Airshow China 2021 in Zhuhai, Guangdong Province. (Image Credit: Global Times)
China’s Hongdu GJ-11 combat drone displayed at the Aviation Industry Corporation, pavilion ahead of Airshow China 2021 in Zhuhai, Guangdong Province. (Image Credit: Global Times)
GJ-11 is jointly designed and developed by China’s Shenyang Aircraft Design Institute (SYADI), Shenyang Aerospace University (SAU), and Hongdu Aviation Industry Group (HAIG). It can carry more than 1,800 kilograms of payload inside its internal weapons bay. This includes air-launched decoys and precision-guided missiles.
China’s People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) also operates GJ-11 from its Type 075 amphibious assault ship, making it one of the few drones in the world that can be operated and stored on naval aircraft carriers.
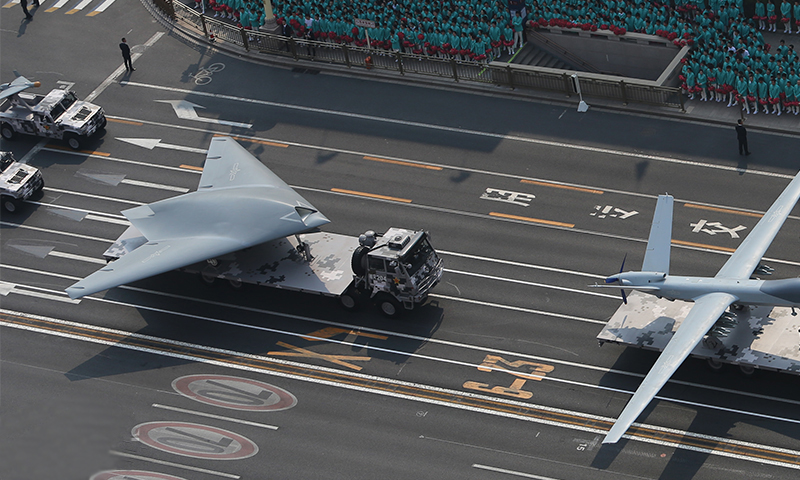 China's GJ-11 stealth attack drone makes during the National Day parade held in Beijing on October 1, 2019. (Image Credit: Fan Lingzhi/GT)
China's GJ-11 stealth attack drone makes during the National Day parade held in Beijing on October 1, 2019. (Image Credit: Fan Lingzhi/GT)
While details of GJ-11 are largely unknown, reported specifications indicate that it has a range of 2,485 miles (4,000 km) and a top speed of 621 mph (1,000 km/h).
S-70 Okhotnik B
Russian-made S-70 Okhotnik (Hunter) is a long-range, stealth combat drone that can carry out reconnaissance, surveillance, and aerial attack missions. The UAV has been developed by the Novosibirsk aviation plant in western Siberia, a subsidiary of the aircraft company Sukhoi. It is equipped with a flat nozzle to increase its stealth capability.
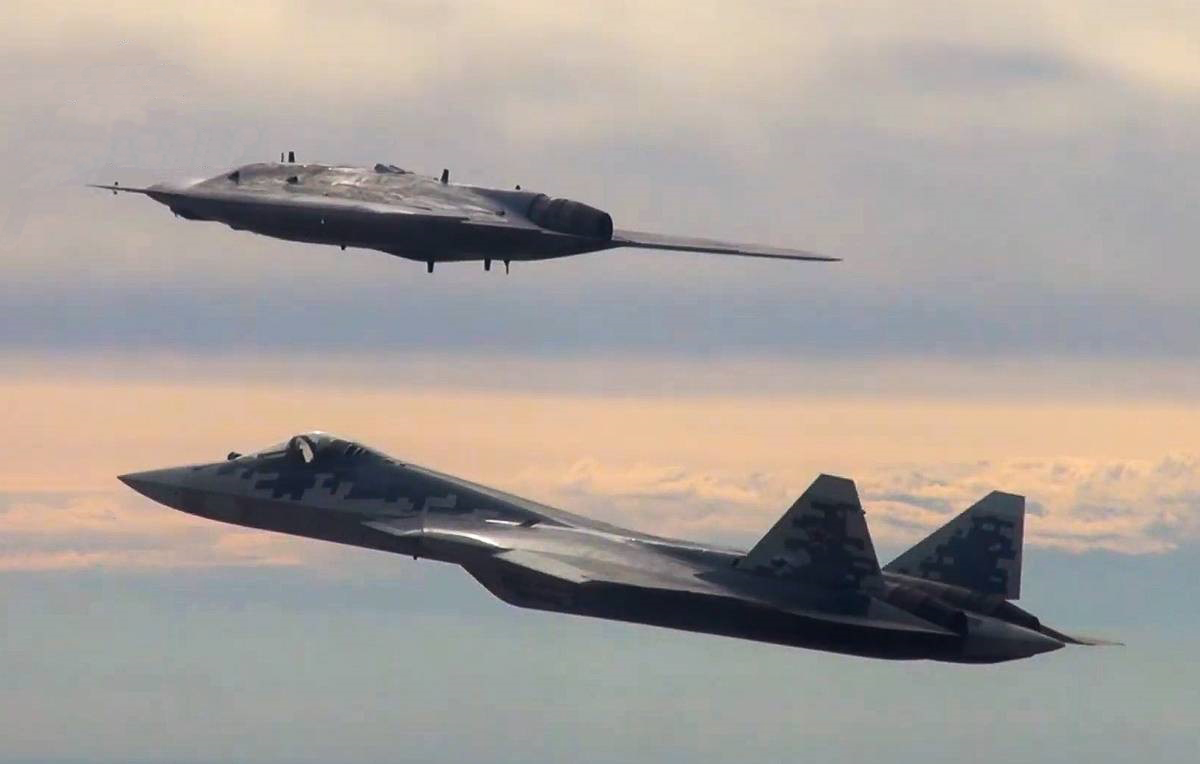 Sukhoi Okhotnik (Hunter) jet-powered unmanned aerial vehicle and the Sukhoi Su-57 jet fighter in action during the first joint flight in Russia. (Image Credit: Russian Defense Ministry)
Sukhoi Okhotnik (Hunter) jet-powered unmanned aerial vehicle and the Sukhoi Su-57 jet fighter in action during the first joint flight in Russia. (Image Credit: Russian Defense Ministry)
Okhotnik’s powerful engine allows the drone to fly more than 6,000 kilometers in a single flight. The Okhotnik drone can also fly collaborative missions with Russian Air Force’s fifth-generation Su-57. The drone can take off with a net weight of twenty tons, making it one of the heaviest combat drones
The drone can reach a maximum speed of approximately 1000 kilometers per hour. So far, two flyable prototype models of Okhotnik B exist. It is expected to be inducted into Russian Air Force by 2024.
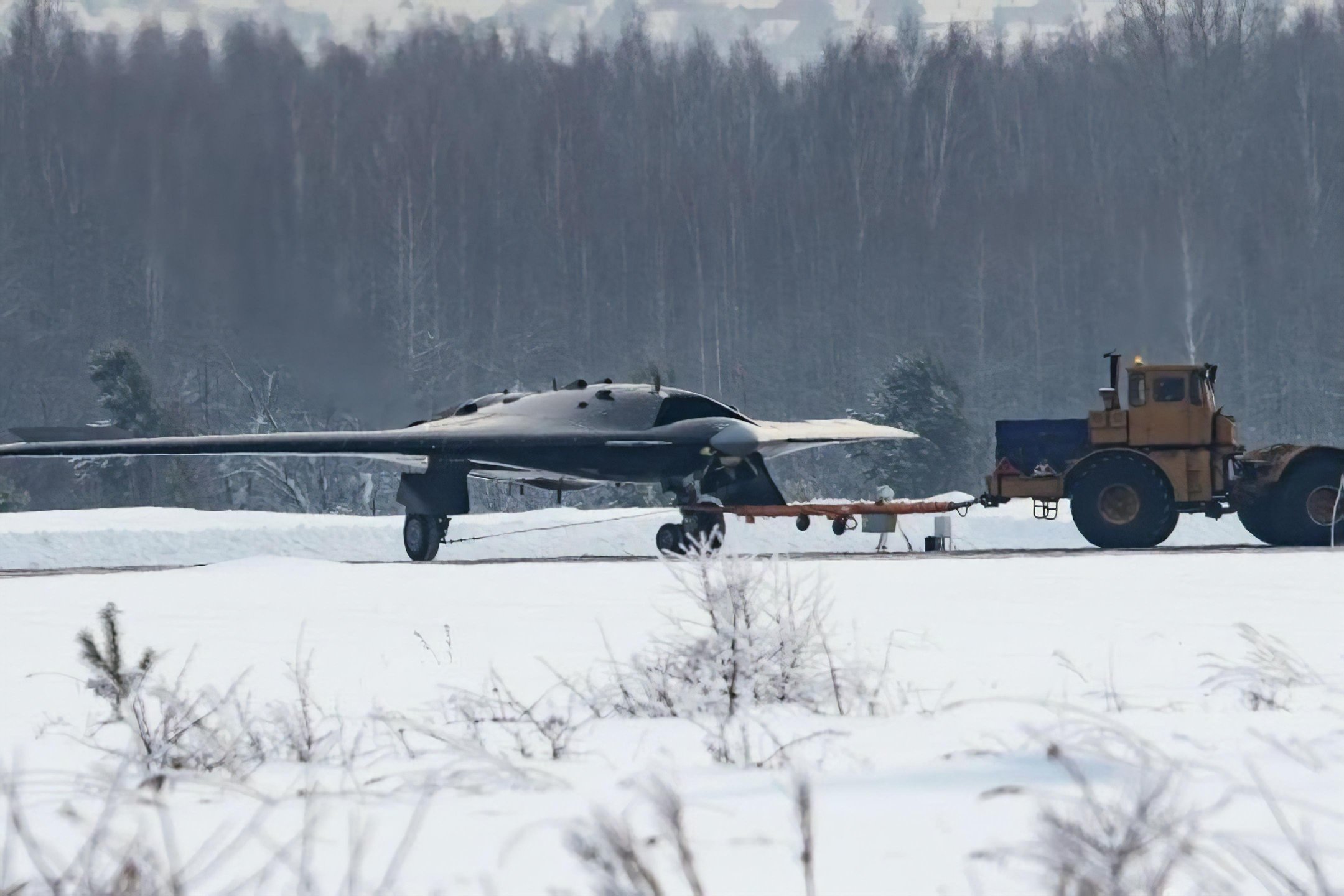 Russian stealth combat drone Okhotnik photographed in far east Russia. (Image Credit: Twitter/@fighter_bomber)
Russian stealth combat drone Okhotnik photographed in far east Russia. (Image Credit: Twitter/@fighter_bomber)
Endurance: 24 hours
Payload capacity: 6,000 kg
Maximum speed: 1,400 km/h
Maximum altitude: 59,000 ft
Primary function: Complex reconnaissance missions and also carry rockets and bombs for strike missions.
RQ-4 Global Hawk
Developed by the makers of the B-2 bomber aircraft, Northrop Grumman’s RQ-4 Global Hawk combat drone is a prime example of a modern remotely-piloted surveillance aircraft. Instead of focusing on packing advanced weaponry and attacking capabilities, the Global Hawk provides a broad overview and systematic surveillance using high-resolution Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Electro-Optical Infrared sensors.
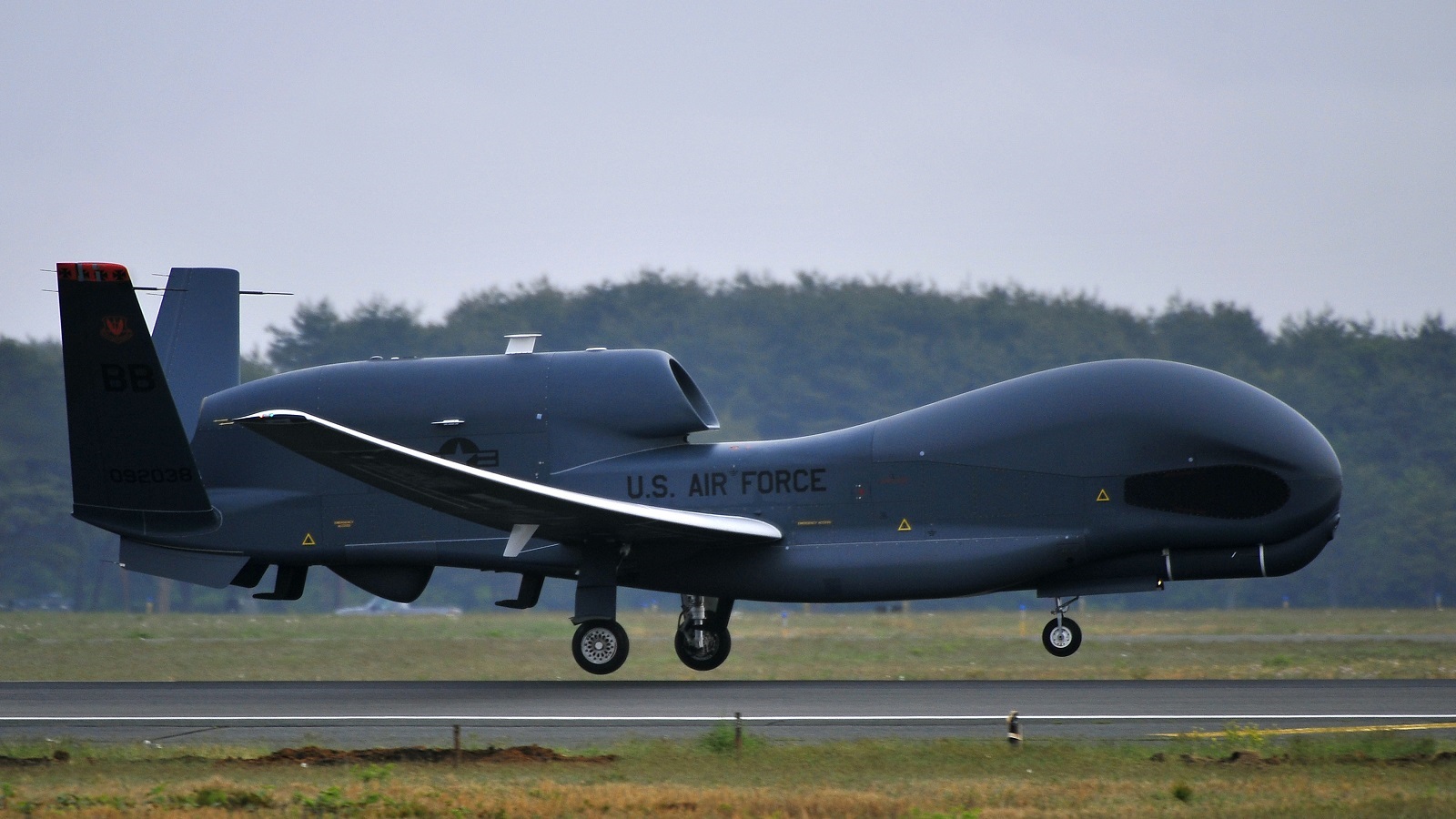 U.S. RQ-4 Global Hawk Drone from Andersen Air Force Base, Guam lands at Misawa Air Base, Japan, May 24, 2014. (Image Credit: U.S. Air Force/Staff Sgt. Nathan Lipscomb)
U.S. RQ-4 Global Hawk Drone from Andersen Air Force Base, Guam lands at Misawa Air Base, Japan, May 24, 2014. (Image Credit: U.S. Air Force/Staff Sgt. Nathan Lipscomb)
This high-altitude and long-endurance drone can survey as much as 40,000 square miles of terrain per day. To put it in perspective, one Global Hawk drone can provide a detailed terrain map for the whole of South Korea in a single day. Due to its highly precise surveillance capabilities, the U.S.-based space agency NASA also uses it to support its high-altitude, long-duration Earth science missions.
Northrop Grumman has also developed EuroHawk, a European variant of its RQ-4 drone with customized sensors. The EuroHawk variant is currently used by the German Air Force and other European forces.
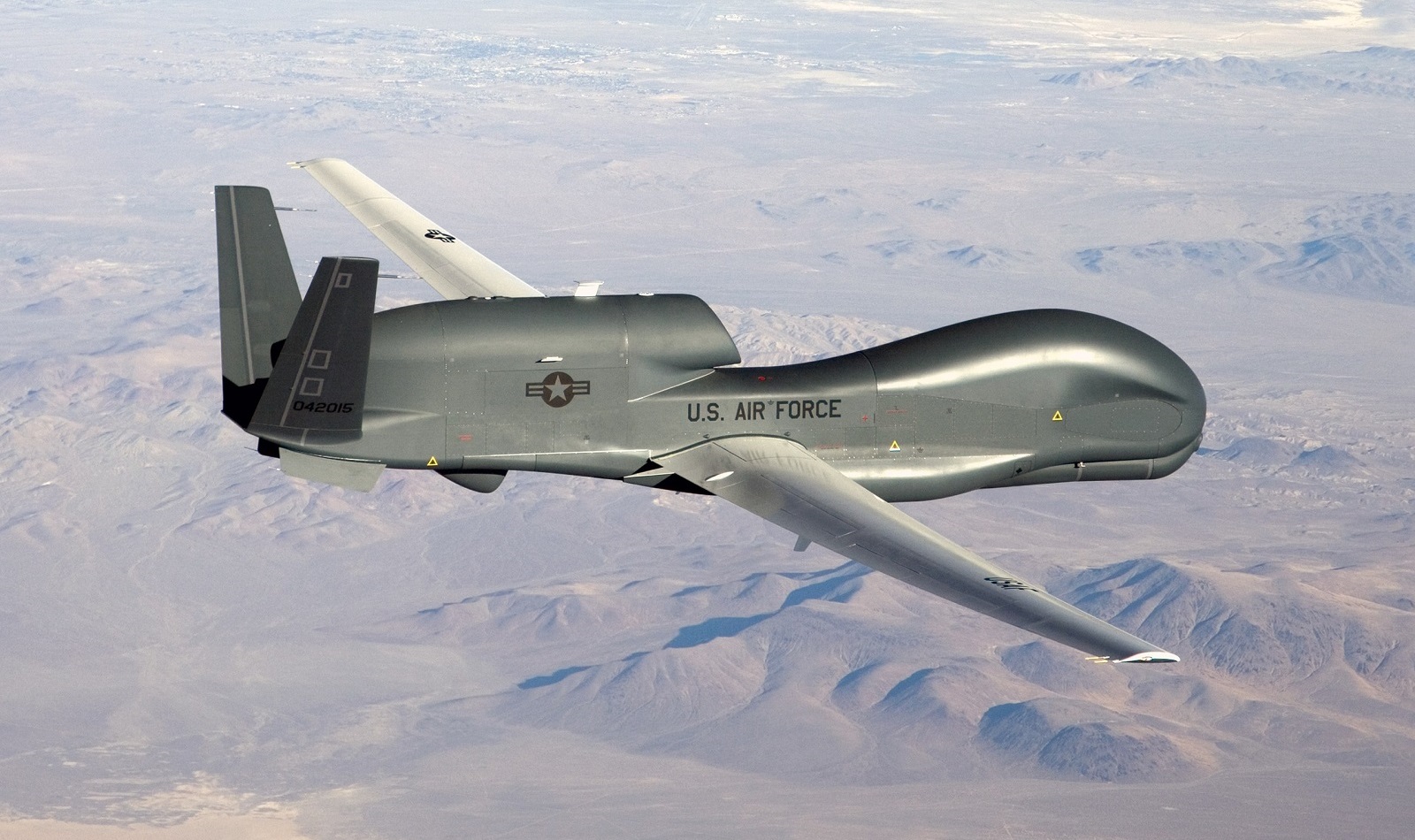 An RQ-4 Global Hawk unmanned aircraft conducting non-military mapping missions. (Image Credit: U.S. Air Force/Bobbi Zapka)
An RQ-4 Global Hawk unmanned aircraft conducting non-military mapping missions. (Image Credit: U.S. Air Force/Bobbi Zapka)
Endurance: More than 34 hours
Payload capacity: 1,360 kg
Maximum speed: 357 mph (575 km/h)
Maximum altitude: 60,000 feet
Primary function: High-altitude and long-endurance ISR.
Wing Loong III
China’s advanced Wing Loong-3 is the first in its series to reach the intercontinental range. The latest variant of the Wing Loong drone series can fly at an impressive maximum range of 10,000 kilometers (6,200 miles) at medium altitude. The drone was first unveiled at the Airshow China 2022 exhibition held in Zhuhai.
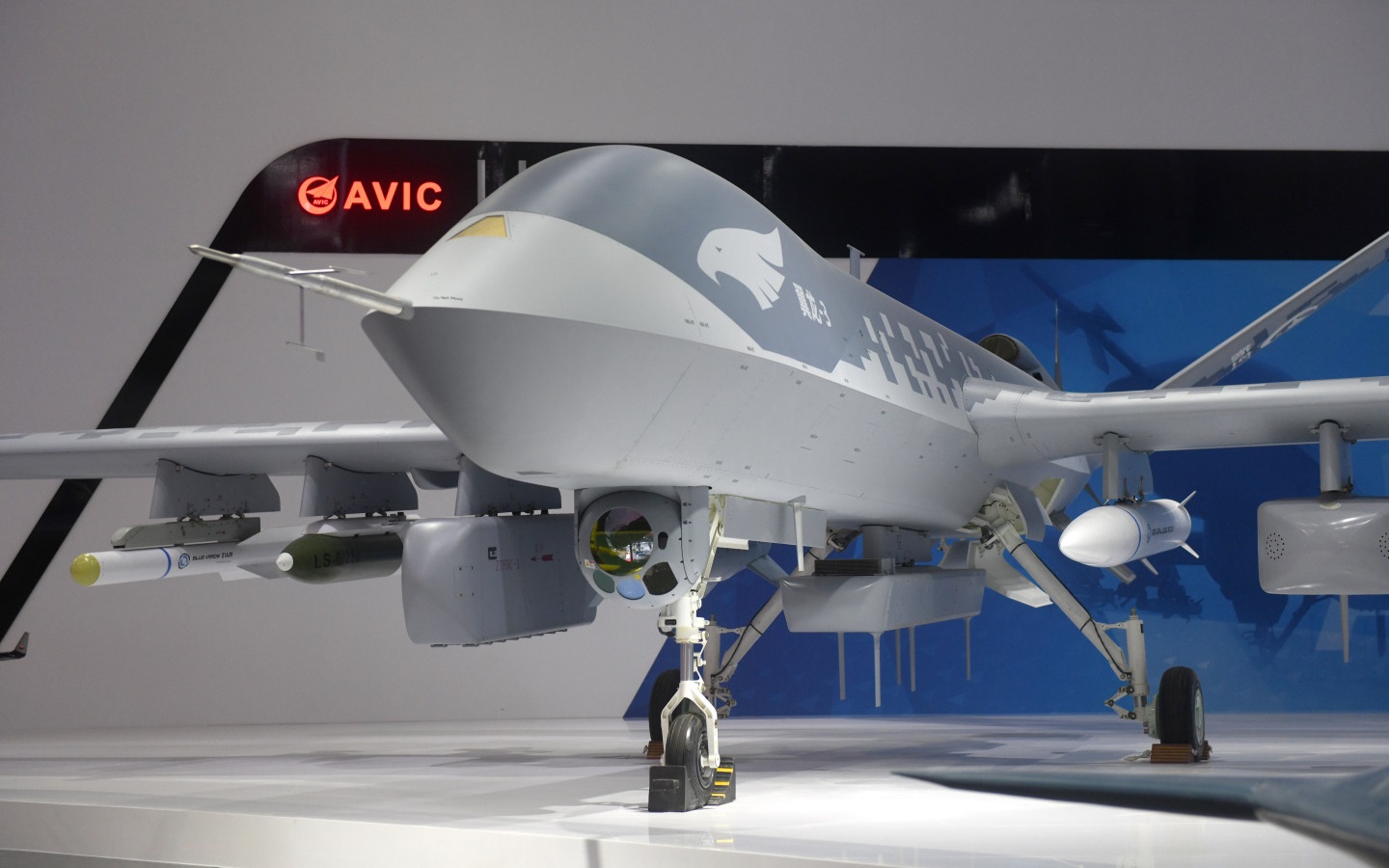 China’s Wing-Loong 3 combat drone during the International Aviation and Aerospace Exhibition in Zhuhai 2022. (Image Credit: Twitter/ChinaDaily)
China’s Wing-Loong 3 combat drone during the International Aviation and Aerospace Exhibition in Zhuhai 2022. (Image Credit: Twitter/ChinaDaily)
Developed by state-owned aerospace and defense firm Aviation Industry Corporation of China (AVIC), the medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) UAV, has a 12.2-meter long main body and a 24-meter wingspan. These features allow the UAV to achieve long-range flight while carrying heavy payloads. It has nine payload hard points and can carry as many as 16 missiles and bombs.
Wing Loong-3’s long-range, heavy payload and multirole capabilities address the requirements of both Chinese and international customers seeking extended mission capabilities and cross-regional long-range flights. The drone can conduct various missions such as maritime escort, anti-submarine operations, aerial fire support, anti-radiation attacks, low altitude alert patrols, electronic reconnaissance, communications relays, and collaborate with manned aircraft and other drones.
 China's AVIC giant Wing Loong 3 unmanned aircraft at Zhuhai International Aviation and Aerospace Exhibition in Guangdong province, China. (Image Credit: Chen Jimin/China News Service)
China's AVIC giant Wing Loong 3 unmanned aircraft at Zhuhai International Aviation and Aerospace Exhibition in Guangdong province, China. (Image Credit: Chen Jimin/China News Service)
Endurance: 40 hours
Payload capacity: 2,300 kg
Maximum range: 6,200 miles (10,000 kilometers)
Primary function: Long-distance surveillance, strikes, and long-duration air patrol.
Elbit Hermes 900
Hermes 900 is a successor to the Hermes 450, a series of drones produced by Israel-based international defense electronics company Elbit Systems. Hermes 900 is a multi-role MALE unmanned aircraft system (UAS) designed for short-range tactical missions.
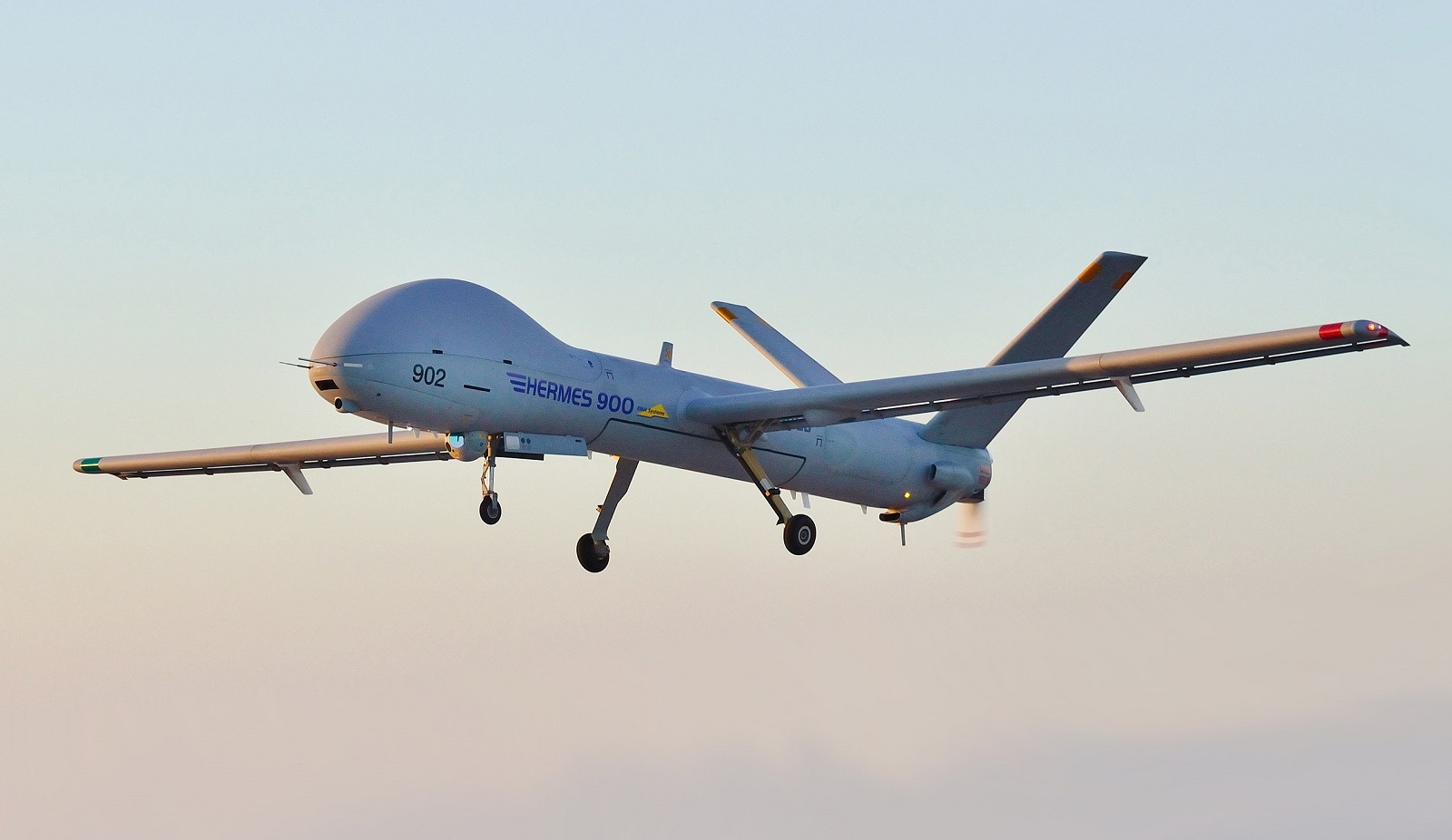 Elbit Systems Hermes 900 Kochav (Star) multi-payload, medium-altitude long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle. (Image Credit: Elbit Systems)
Elbit Systems Hermes 900 Kochav (Star) multi-payload, medium-altitude long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle. (Image Credit: Elbit Systems)
The drone has an endurance of more than 30 hours and can fly at an altitude of 30,000 feet. With a payload capacity of 350 kilograms, the system excels in performing vital tasks such as area dominance, persistent intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR). The drone is equipped with several high-tech infrared and electro-optical sensors.
Elbit Hermes 900 has been in service with the Israeli Air Force since 2012. Due to its low cost and high endurance, several countries have made deals with Elbit to procure the Hermes 900 drone. The list includes Azerbaijan, Chile, Brazil, Canada, Iceland, the Philippines, and Switzerland.
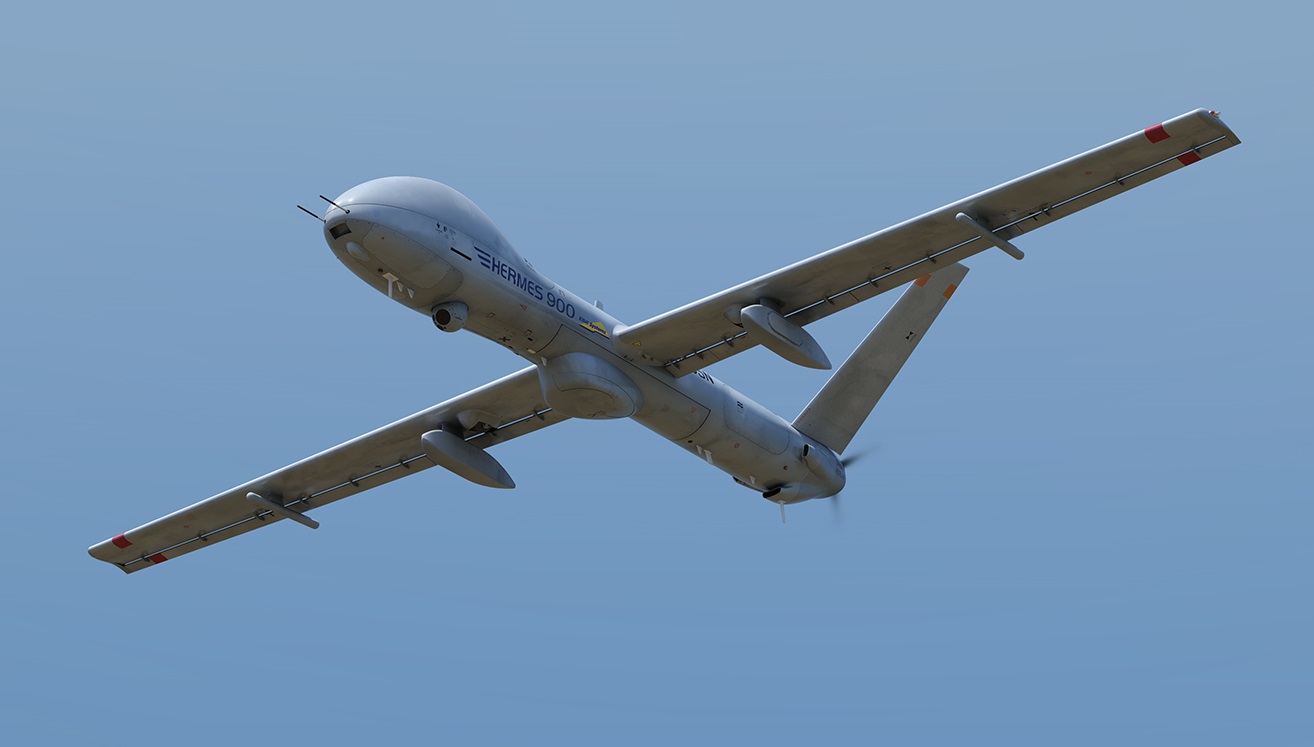 Israel’s next-generation multi-role Hermes 900 unmanned aerial vehicle. (Image Credit: Elbit Systems)
Israel’s next-generation multi-role Hermes 900 unmanned aerial vehicle. (Image Credit: Elbit Systems)
Endurance: Up to 36 hours
Payload capacity: 350 kg
Maximum speed: 220 km/h
Maximum altitude: 9,144 m (30,000 ft)
Primary function: Intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance.
Shahed 129
Iran has recently emerged as a bulk drone manufacturer. Most of the Iranian drones are cheaper and disposable, widely used by the Russian forces during their invasion of Ukraine. However, standing out among its array of inexpensive Kamikaze drones is Iran’s Shahed 129 — a multirole drone capable of carrying out reconnaissance missions and precision air-to-ground strikes with small guided munitions.
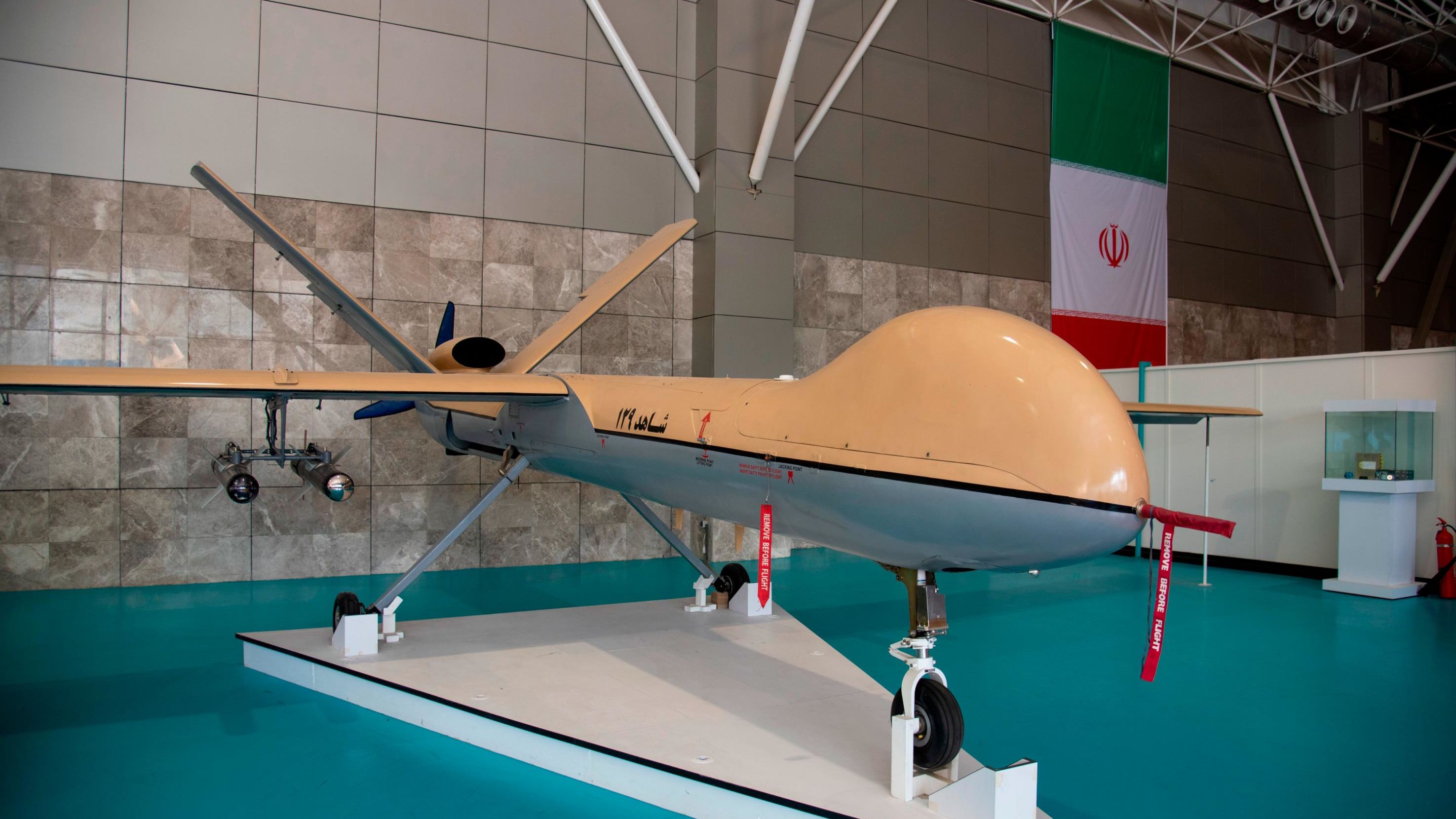 An Iranian Shahed-129 drone on display at the IRGC aerospace fair in Tehran on June 28, 2021. (Image Credit: ISNA/Pacific Press)
An Iranian Shahed-129 drone on display at the IRGC aerospace fair in Tehran on June 28, 2021. (Image Credit: ISNA/Pacific Press)
Shahed 129 is a single-engine Medium Altitude Long Endurance UAV designed by Shahed Aviation Industries. Iran has reportedly used this drone for both external and internal missions since unveiling the drone in September 2012.
Iran has not released much information about the drone, however, experts believe that the design and making of Shahed 129 are highly inspired by the U.S.-made MQ-1 Predator and Israel’s Hermes 450 drones. The UAV’s maximum range reaches 1,700 km and a flight endurance of about 24 hours.
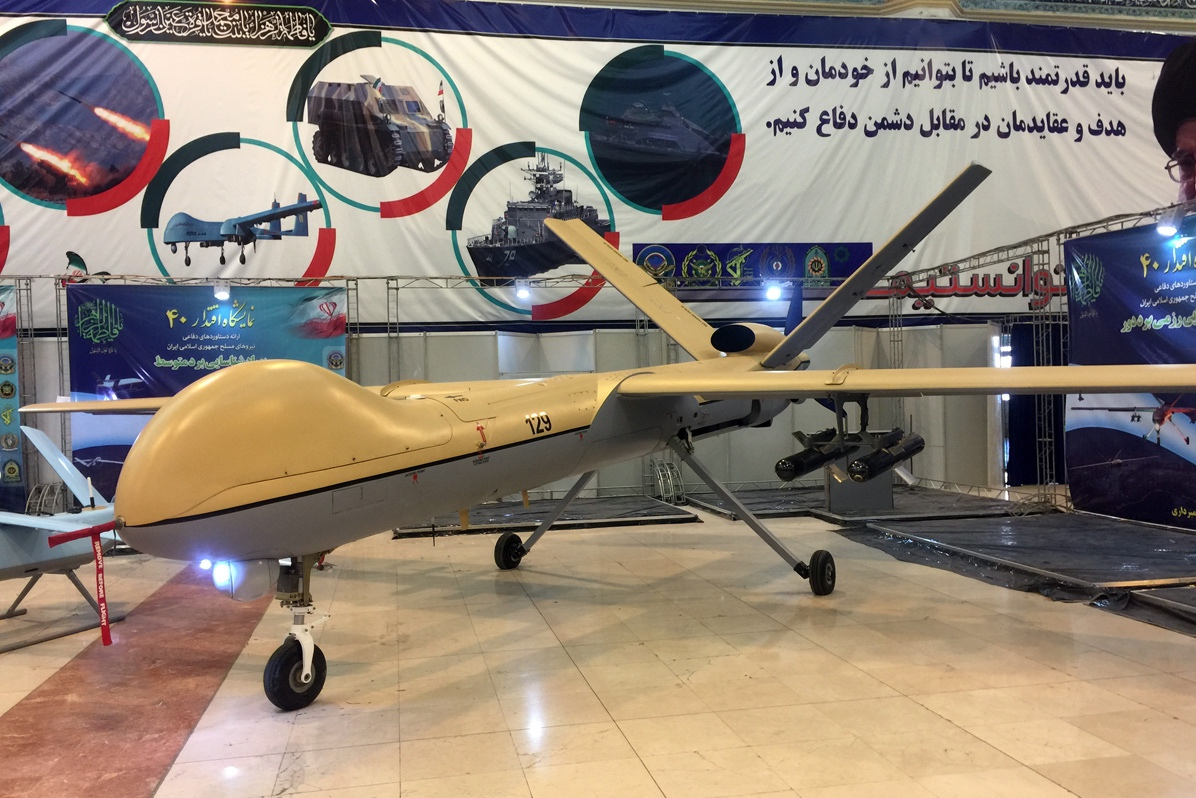 Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industries Corporation's second generation Shahed 129 combat drone. (Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Iran Aircraft Manufacturing Industries Corporation's second generation Shahed 129 combat drone. (Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
Endurance: 24 hours
Payload capacity: 400 kg
Maximum speed: 150 km/h
Maximum altitude: 7,300 m (24,000 ft)
Primary function: Combat or intelligence and surveillance missions.
Kronshtadt Orion
Orion is a relatively smaller drone developed by Russia’s Kronshtadt Group under a project funded by the Russian Ministry of Defense. Kronshtadt started the development of Orion in 2011. The first prototype took to the skies in 2016 and the drone was inducted into the Russian Air Force in 2020.
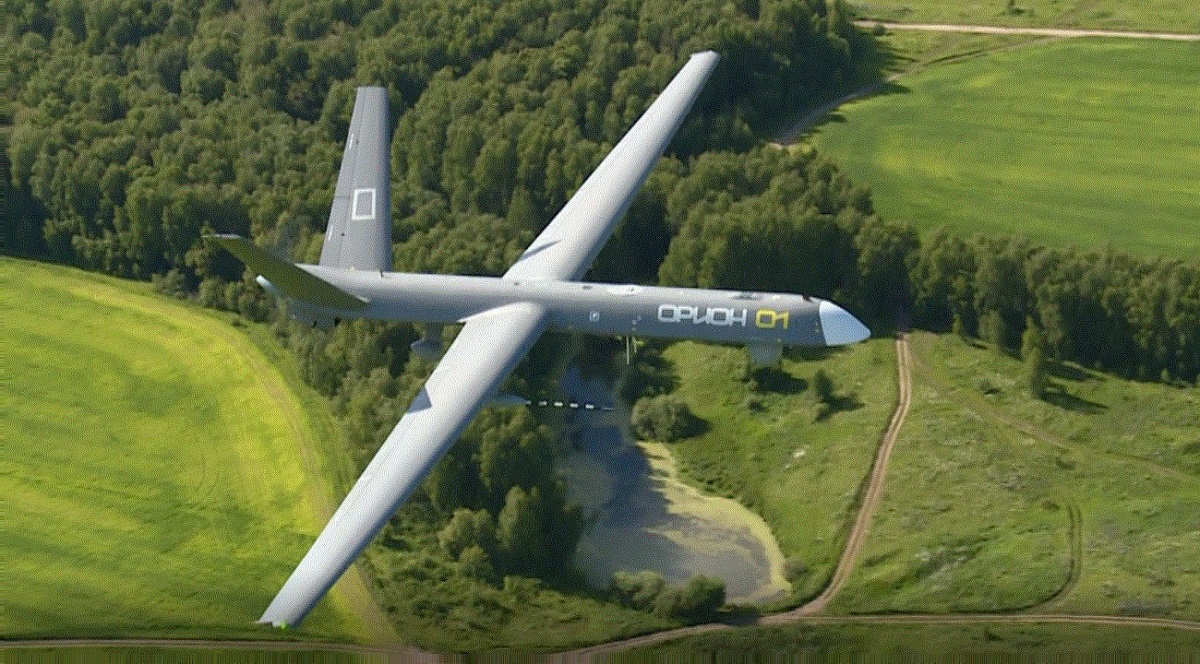 Russia's Orion medium-altitude, long-endurance military drone. (Image Credit: KT Group)
Russia's Orion medium-altitude, long-endurance military drone. (Image Credit: KT Group)
Orion-E is a medium-altitude long-endurance UAV. It is primarily an Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) system equipped with sensors to map the terrain and transmit coordinate targets.
With 8 meters of length and 16 meters of wingspan, Orion can carry 250 kilograms of payload. It has a maximum speed of 120 kilometers per hour and a cruising speed of 200 kilometers per hour. The drone can also be modified to carry missiles and other armaments. Kronshtadt has also developed Vikhr-1V guided missiles for its Orion drone.
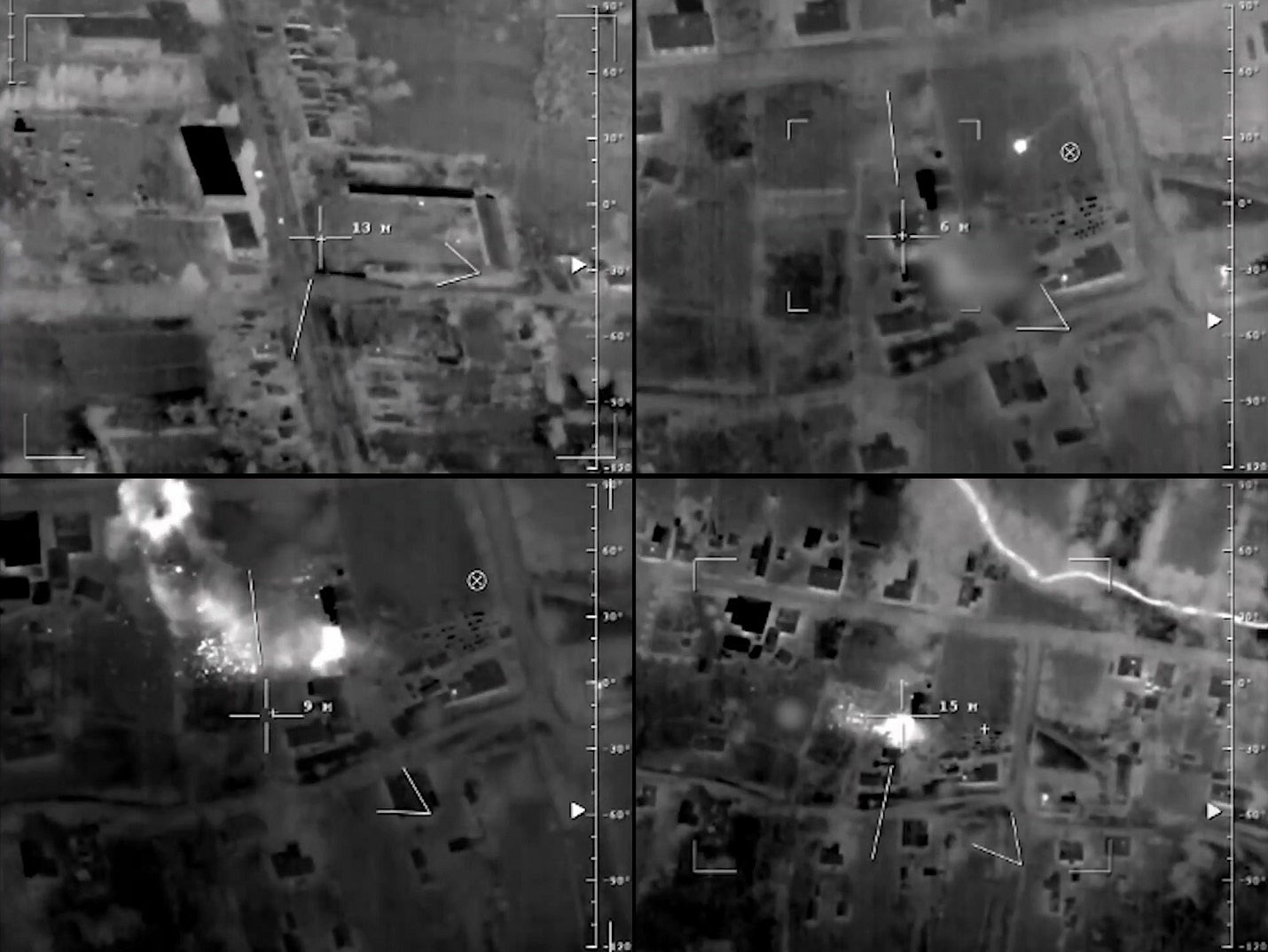 Video grab of Russian Orion drone destroying the Aidar command post of the nationalist battalion. (Image Credit: Russian forces/Video grab by IRIA)
Video grab of Russian Orion drone destroying the Aidar command post of the nationalist battalion. (Image Credit: Russian forces/Video grab by IRIA)
Endurance: 24 hours
Payload capacity: 200 kg
Maximum speed: 120 km/h
Maximum altitude: 7,500 m (24,600 ft)
Primary function: Day and night aerial intelligence and surveillance missions.
BAE Systems Taranis
Under development by the British aerospace and arms manufacturer, BAE Systems, the Taranis aims to become an intercontinental combat mission drone. The drone has been named after the Celtic God of thunder. The first working prototype of Taranis was unveiled in 2013. The British Ministry of Defense is yet to comment on the success of the drone trials and the completion of its induction into the military. With a wingspan ranging up to 10 meters and a length of 12 meters with 4 meters of height, Taranis would be one of the biggest jet-powered drones in the world.
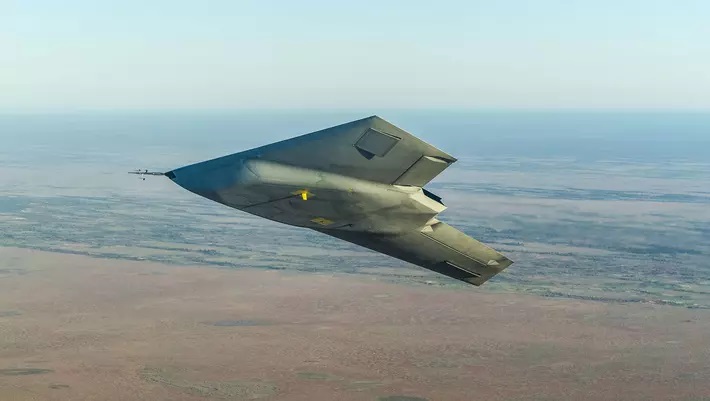 An unmanned combat aircraft system Taranis with advanced technology demonstrator program. (Image Credit: BAE Systems)
An unmanned combat aircraft system Taranis with advanced technology demonstrator program. (Image Credit: BAE Systems)
The Taranis program was started by BAE Systems back in 2005 when the United Kingdom released its defense strategy stressing the importance of developing UAVs. However, due to economical alternative options, the project took a backseat over the years. With a renewed wave of military modernization and increased emphasis on combat drones, it is expected that the Taranis drone would soon be completed and inducted into military use.
Length: 12.43 m (41 ft)
Wingspan: 10 m (33 ft) (approximate)
Height: 4 m (13 ft)
Armament: 2 x internal missile bay provision.
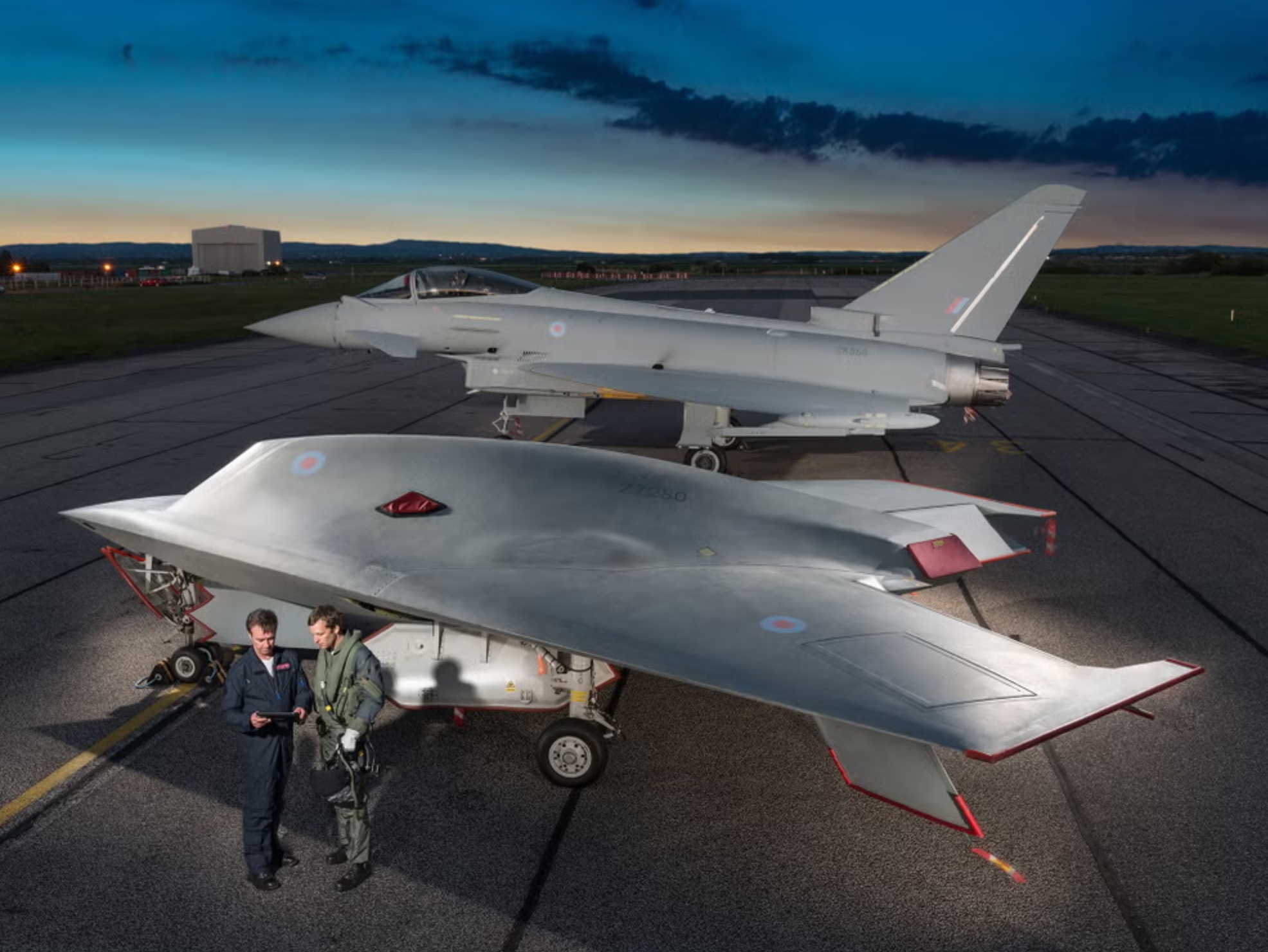 An unmanned Taranis drone in front of a piloted fighter jet. (Image Credit: BAE Systems)
An unmanned Taranis drone in front of a piloted fighter jet. (Image Credit: BAE Systems)
ALSO READ:
Regions
Issues